- The setup: scene and cameras
 |
Two cameras are looking at each other, capturing a hall between them with people walking, sitting down and rising.
- Input sequences
| Camera 1 | Camera 2 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| Synchronized video:MPEG 730Kb | |
- Detect moving objects
... using background subtraction:| Camera 1 | Camera 2 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| Synchronized video: GIF 310Kb | |
- Extract interest points
... by taking the highest point on each blob, in each frame:| Camera 1 | Camera 2 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Construct trajectories from these points
| Camera 1 | Camera 2 |
|---|---|
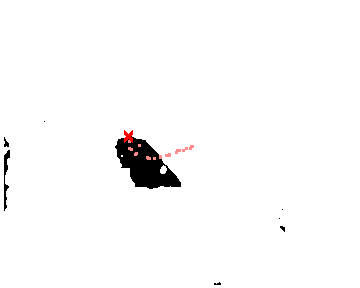 |
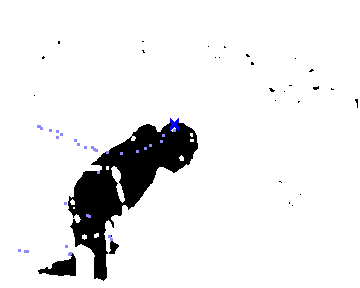 |
| Synchronized video: GIF 310Kb | |
- Use the trajectories as features for matching algorithm
| Camera 1 | Camera 2 |
|---|---|
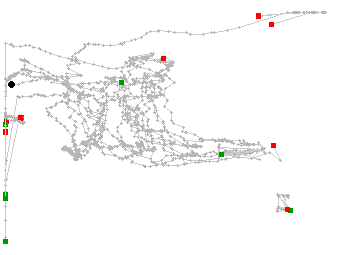 |
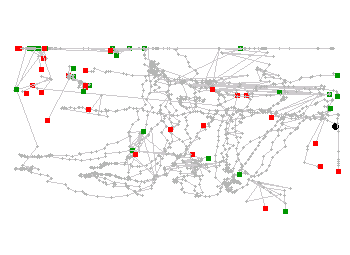 |
There are 11 trajectories for camera 1, and 28 trajectories for camera 2.
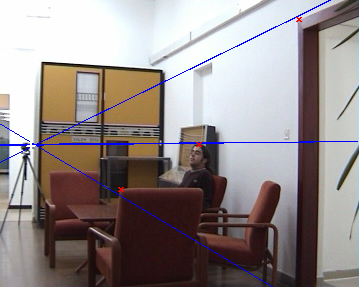
- Recover epipolar geometry (spatial alignment)
| Camera 1 | Camera 2 |
|---|---|
 |
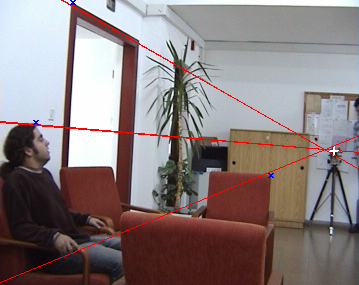 |
blue points on the right correspond to the blue lines on the left (their epipolar lines).
Points are manually put and their epipolar lines calculated using recovered fundamental matrix.
White cross marks location of the opposite camera (the ground-truth epipole).